Renal infarcts are often incidental findings in animals with chronic renal disease. Infarcts are caused by thrombi that occlude a blood vessel in the kidney. Most of the time, they are chronic and mainly made up of fibrous tissue. The classic appearance is of a hyperechoic, wedge shaped area with the wide part of the triangle at the kidney capsule. The capsule is also usually concave at the site because of fibrosis and loss of normal renal parenchyma.
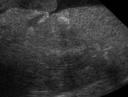
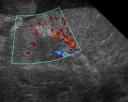
Acute renal infarcts have the same etiology, but we are seeing them within a few days after they occur. What do they look like? They are more subtly hyperechoic than the chronic infarct. In image 1, the infarct is visible as an indistinct, hyperechoic wedge in the cortex of the kidney. The medulla is out of plane so most of what is visible is cortex. The second image is a color Doppler display of the blood flow in the renal vessels. You can see the signal disruption and partial void in the hyperechoic are that represents the infarct. This dog had a systemic neoplasia with infarcts affecting the kidneys and other organs. Acute renal infarcts don’t alter the shape of the renal cortex.
Recent Comments